behaviour of ductile and brittle materials in compression test|brittle ductile transitions : export for ductile materials, asymmetric response in tension-compression for brittle materials with higher strength in compression, no plastic yielding, etc. Consider the case of a ductile material. web29 de set. de 2023 · A mentor is an individual who acts as an adviser or coach for a less experienced or advanced mentee, providing expertise and professional knowledge from a more experienced perspective. At the core of the relationship, a mentor is available to their mentee to offer advice, provide support and answer questions.
{plog:ftitle_list}
O Fortune Mouse Demo é uma versão de demonstração fascinante de um dos slots mais populares, atraindo jogadores com sua temática encantadora e jogabilidade envolvente. .
ductile materials theory pdf
A derivation of the failure surface orientations from a particular isotropic materials failure theory reveals that uniaxial tension has its ductile/brittle transition at T / C = 1/2, where T and C are the uniaxial strengths.19.4 Brittle Failure Under Static Loads. Many cast materials, such as gray cast iron, are brittle but have compressive strengths much higher than their tensile strengths (uneven material) Low . This paper aims to investigate the link between brittle-ductile transition stress, uniaxial compressive strength and Hoek–Brown material constant (mi) for different kinds of .
Different approaches have been used to study fracture of brittle and quasi-brittle materials in compression. We review these and assess the limitations of each approach. We .
for ductile materials, asymmetric response in tension-compression for brittle materials with higher strength in compression, no plastic yielding, etc. Consider the case of a ductile material.
Multi-axial stress states that are generally compressive are found to be generally ductile whereas multi-axial stress states that are generally tensile are also generally brittle. There is logic and organization to the overall . The micromechanics of brittle failure in compression and the transition from brittle to ductile failure, observed under increasing confining pressures, are eaxamined in the light of. In this work, a series of uniaxial compression tests were performed to investigate the effect of infilling composition (i.e., proportion and grain size) on the mechanical responses .
The JH-2 constitutive model is selected to model the brittle materials, which is developed to study the stress-strain behavior of brittle materials (such as ceramics, glass .
In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain.It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and . Understanding the size dependence of quasi-brittle materials' fracture behavior is useful in assessing the safety of flawed rock engineering structures. In this study, a set of uniaxial compression tests were conducted to scrutinize the mechanical properties and crack morphology of cubic specimens with sizes of 75 mm, 100 mm, 125 mm and 150 mm. The .
Tensile test of an Al-Mg-Si alloy.The local necking and the cup and cone fracture surfaces are typical for ductile metals. This tensile test of a nodular cast iron demonstrates low ductility.. Ductility refers to the ability of a material to .There are two types of fracture: brittle fracture and ductile fracture. Brittle fracture involves crack growth with little or no ductile deformation of the material around the crack tip. This is an undesirable mode of fracture because brittle cracking can lead to complete failure of the material very rapidly when a critical load is reached. The stress-strain curve is a fundamental mechanical representation that elucidates the behaviour of materials under applied load, offering insights into their deformation characteristics. This curve unveils a distinct mechanical response marked by minimal plastic deformation and a sudden, catastrophic failure in the context of brittle materials, such as .Stress–Strain Behavior of Ductile and Brittle Materials Ductile Materials. Any material that can be subjected to large strains before it fractures is called a ductile material. Mild steel, is a typical example. Engineers often choose ductile materials for design because these materials are capable of absorbing
There are crucial differences between the tensile and compressive failures of quasi-brittle materials. Intermolecular or interatomic bonds have to be stretched to be broken and can break when the maximum bond strength is reached: compressing such bonds will not break them [1].This latter point is demonstrated by considering the application of hydrostatic compression .MATERIAL FAILURE (a) test y y E 1 (b) Ductile (c) Brittle Figure 5.1: Uni-axial stress-strain response for ductile and brittle materials. The basic question in this case is: For general stress states (e.g. solutions to 2D or 3D elasticity problems), for what combinations and intensities of stress components will the material start yielding .

brittle material failure pdf
The topic of stress-strain behaviour of ductile and brittle materials contained concepts of engineering stress and strain, the stress-strain pat- tern of metals, engineering properties and . Similarly, pressure can be used to control ductile-brittle effects. Sufficiently large superimposed pressure can convert a generally brittle material into a ductile material.[11] Metals like aluminum, gold, silver, and copper have a face-centered cubic crystal lattice structure, and most do not experience a shift from ductile to brittle behavior.Similarities and differences between ductile material and brittle material are provided in this article. At a particular temperature, a ductile material exhibits substantial plastic deformation under external loading, while a brittle material breaks .Constitutive Material Response: Linear elasticity and Hooke’s Law. The mechanical response of a material is characterized experimentally. A mathematical relation between the components of the stress and the strain tensor is sought. We have already discussed the. uniaxial stress test and the general characteristics of the corresponding
Compression Test The goal of a compression test is to determine the behavior or response of a material while it experiences a compressive load by measuring fundamental variables, such as, strain, stress, and deformation. Uniaxial compression tests provide much of the same information about material properties as tension tests.
The stress-strain curve for ductile materials serves as a fundamental depiction of the mechanical behaviour and response of materials subjected to external forces. Ductile materials exhibit a unique resilience in the face of applied stress, with the ability to undergo substantial deformation before eventual fracture.Bending behavior of ductile materials. . In order to check the strength of brittle materials, the bending test is often more suitable than the tensile test, because the materials are subjected to bending stress only. If this sample .How do ductile and brittle materials behave in compression test? Since the greatest shear stresses occur at an angle of 45° to the direction of compressive stress, brittle specimens usually fracture along this direction. The onset of a crack in ductile materials or the sudden break in brittle specimens is characterized by the so-called .Brittle fracture or brittle failure is used by them to qualitatively describe the post-peak failure process (i.e. brittle-ductile transition) of rock in the compression test (Fig. 1). Brittle .
Understand what brittle means. Learn the differences between ductile and brittle materials. Know what a ductile fracture is and discover materials. Ductile fractures generally occur in metals and some polymers. In fact, the final failure mode is often essentially brittle, as the capacity for ductile behavior is exceeded. Brittle Fractures: Brittle fractures occur in materials that exhibit minimal (often no) plastic deformation prior to cleavage. The absence of necking, a flat or glossy .
Composite patch repair using natural fiber for aerospace applications, sustainable composites for aerospace applications. Mohd Khirul Hafiz Muda, Faizal Mustapha, in Sustainable Composites for Aerospace Applications, 2018. 9.13 Compression test. Compression testing is one of the most important tests to determine the behavior of composite materials. . Mechanical properties of . I was reading the book Mechanics of Materials by Beer and Johnston.The author points out in torsion chapter that ductile materials generally fail in shear.And brittle materials materials are weaker in tension than in shear.From this they concluded that when subjected to torsion a circular shaft made of ductile material breaks along a plane perpendicular to it's .In this case we have to distinguish between stress-strain characteristics of ductile and brittle materials. The following points describe the different regions of the stress-strain curve and the importance of several specific locations. . Some steels and other materials exhibit a behaviour termed a yield point phenomenon. Yield strengths vary .
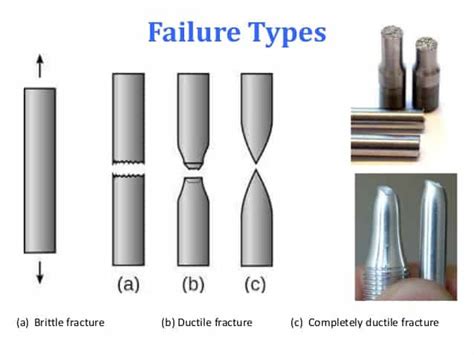
Standard specimen, elastic and plastic range, stress, strain and strain rate, brittle and ductile materials in compression. Advantages over tension test. Bauschinger effect. Barreling and buckling in compression test and remedial measures against them. Critical.
With a brittle material, tensile testing may give an approximately linear stress-strain plot, followed by fracture (at a stress that may be affected by the presence and size of flaws). . how the behaviour can be accurately captured and the stress and strain fields explored at any point during the test.(These two materials will also be used to .
The micromechanics of brittle failure in compression and the transition from brittle to ductile failure, observed under increasing confining pressures, are examined in the light of existing experimental results and model studies. First, the . Examples of ductile materials include mild steel, aluminium, and gold. A material is brittle if it fractures at low strains with little or no plastic deformation. Examples of brittle materials include glass and ceramics. The differences between ductile and brittle materials can be seen in the stress-strain curves shown below.The Basic Properties of Building Materials. In Building Materials in Civil Engineering, 2011. 1 Brittleness. Brittleness describes the property of a material that fractures when subjected to stress but has a little tendency to deform before rupture. Brittle materials are characterized by little deformation, poor capacity to resist impact and vibration of load, high compressive .
Resultado da Veja as últimas notícias, vídeos e entrevistas sobre maria cândida fonseca na Jovem Pan
behaviour of ductile and brittle materials in compression test|brittle ductile transitions